반응형
This page introduce FFT sourece code.
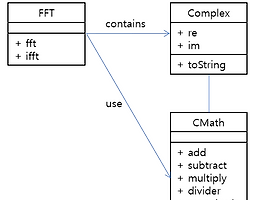
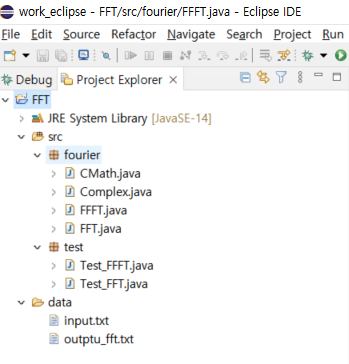
There are 4 java soure file and 1 text file.
- fourier/FFT.java
- fourier/Complex.java
- fourier/CMath.java
- test/Test_FFT.java
- data/input.txt
1. fourier/FFT.java
package fourier;
public class FFT {
private static double log2(double a) {
return Math.log(a) / Math.log(2);
}
/**
* Check the number is power of 2 or not.
* @param N
* @return
* 0 : it is power of 2
* padding_count: if it is now power of 2, required count number to be power of 2
* @throws Exception
*/
private static int checkPowerOfTwo(int N) throws Exception {
int result = -1;
if (N == 0) throw new Exception("Input size is zero.");
double l,c,f;
l=FFT.log2(N);
c=Math.ceil(l);
f=Math.floor(l);
if(c==f) result =0;
else result = (int)Math.pow(2, c)-N;
return result;
}
private static Complex[] makePowerOfTwoSize(Complex[] arr, int fillCount) {
Complex[] newArr = new Complex[arr.length + fillCount]; //initial value is null
System.arraycopy(arr, 0, newArr, 0, arr.length);
for(int i=arr.length;i<newArr.length;++i) {
newArr[i] = new Complex(0,0);
}
return newArr;
}
// getReversedArr(13,4) -> {1,0,1,1} where, 13=1101
private static int getReversedNum(int num, int numOfBits) {
int i, j, k;
//1. Decimal number -> Reversed Binary array
byte a;
int d=0;
//num=13, numOfBits=4
for (i=0;i<numOfBits;++i) { // 0 1 2 3
j = numOfBits - 1 - i; // 3 2 1 0
k = (int)(num >> j); // 13>>3=1 13>>2=3 13>>1=6 13>>0=13
a = (byte)(k & 1); // arr[3]=1 arr[2]=1 arr[1]=0 arr[0]=1
d = d + (a<<i);
}
return d;
}
private static Complex[] arrange4fft(Complex[] src, int numOfBits) throws Exception{
int i,j;
Complex[] arrangedSrc = new Complex[src.length];
for(i=0;i<src.length;++i) {
j = FFT.getReversedNum(i, numOfBits); //{000,001,010, 011, 100, 101, 110, 111} -> {0, 4, 2, 6, 1, 5, 3, 7}
arrangedSrc[j] = src[i];
}
return arrangedSrc;
}
/**
* Calculate W(Convolution ring)
*
* W[k] for FFT = cos(theta) - isin(theta), where theta = (2pi*k/N)
* W[k] for IFFT = cos(-theta) - isin(-theta), where theta = (2pi*k/N)
* @param N
* @param isInverse true: for IFFT, false: for FFT
* @return calculated W array
*/
private static Complex[] calculateW(int N, boolean isInverse) {
Complex[] W = null;
double T = 0;
int N2 = N/2;
W = new Complex[N2];
T = 2 * Math.PI / N;
double theta = 0;
if (isInverse) { //IFFT
for(int i=0;i<N2;++i) {
theta = -(T * i);
W[i] = new Complex(Math.cos(theta), -Math.sin(theta));
}
}else { //FFT
for(int i=0;i<N2;++i) {
theta = (T * i);
W[i] = new Complex(Math.cos(theta), -Math.sin(theta));
}
}
return W;
}
/**
*
* @param X 2D array. X[0][] and X[1][] change it's role each other by the src and tgt number
* @param src source index of the array X. 0 or 1
* @param tgt target index of the array X. 0 or 1
* @param s Starting index of the data in the array
* @param size Region size to be calculated: 2 -> 4 -> 8 -> ...
* @param kJump k's jumping value to use right value of W
* @param W Convolution ring
*/
private static void regionFFT(
Complex[][] X, int src, int tgt, int s, int size, int kJump, Complex[] W) {
// Xm+1[i] = Xm[i] + Xm[i+half]W[k]
// Xm+1[i+half] = Xm[i] - Xm[i+half]W[k]
int k=0;
int e = s + (size/2)-1;
Complex T=null;
int half = (int)(size / 2);
for(int i=s;i<=e;++i) {
T = CMath.multiply(X[src][i+half], W[k]);
X[tgt][i] = CMath.add(X[src][i], T);
X[tgt][i+half] = CMath.subtract(X[src][i], T);
k += kJump;
}
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////
private static Complex[] fft_forward(Complex[] src, boolean isInverse) throws Exception {
int N = src.length;
//1. check src data size. If it's not 2^n size then make it to be 2^n size with zero padding
int fillCount = 0;
fillCount = checkPowerOfTwo(N);
if(fillCount > 0) {
src = makePowerOfTwoSize(src, fillCount);
}else if(fillCount < 0) {
throw new Exception("Something wrong: while calculateing filling count from the input data");
}
//2. calculate loop count: 2-> 1, 4->2, 8->3, 16->4
N = src.length; //input array can be changed. so, read one more time.
int totalLoop = (int)FFT.log2(N); //it is guaranteed that N is 2^n number, therefore log2(N) will be int value.
//3. arrange src index to calculate FFT as bottom-up style
Complex[] arrangedSrc = arrange4fft(src, totalLoop);
//4. calculate W: 0 to (N/2-1)
Complex[] W = calculateW(N, isInverse); //for fft. for ifft:calculateW(N, true)
//5. use 2-dimensional array to save memory space. X[0, ] <-> X[1, ]
Complex[][] X = new Complex[2][N];
System.arraycopy(arrangedSrc, 0, X[0], 0, N);
//6. calculate FFT by bottom-up style
int srcIdx=0, tgtIdx=0;
int kJump=0, regionSize =0;
for(int curLoop=0; curLoop<totalLoop;++curLoop) {
tgtIdx = (tgtIdx+1) % 2;
srcIdx = (tgtIdx+1) % 2;
regionSize = 1 << (curLoop+1); //if N=8: 2 -> 4 -> 8
kJump = 1 << (totalLoop - curLoop - 1); //if N=8: 4 -> 2 -> 1
int i=0;
while(i<N) {
regionFFT(X, srcIdx, tgtIdx, i, regionSize, kJump, W);
i += regionSize;
}
}
//7. find final output index in the X array
int resultIdx = ((totalLoop & 1) == 0) ? 0 : 1;
//8. in case of IFFT, divide N
if(isInverse) {
for(int i=0;i<N;++i) X[resultIdx][i] = CMath.divideR(X[resultIdx][i], N);
}
//9. return the result as 1d array
return X[resultIdx];
}
public static Complex[] fft(double[] src) throws Exception{
return FFT.fft(src, -1);
}
public static Complex[] fft(double[] src, int roundDigit) throws Exception{
Complex[] complexSrc = new Complex[src.length];
for(int i=0;i<src.length;++i) complexSrc[i] = new Complex(src[i],0);
Complex[] X = fft_forward(complexSrc, false);
// round up at roundDigit
if(roundDigit >= 0) {
double d = Math.pow(10.0, roundDigit);
for(int i=0;i<X.length;++i) {
X[i] = new Complex(Math.round(X[i].re * d)/d, Math.round(X[i].im * d)/d);
}
}
return X;
}
public static double[] ifft(Complex[] src) throws Exception{
return FFT.ifft(src,-1);
}
public static double[] ifft(Complex[] src, int roundDigit) throws Exception{
Complex[] complexArr = fft_forward(src, true);
double[] x = new double[complexArr.length];
if(roundDigit >= 0) {
double d = Math.pow(10.0, roundDigit); // round up at roundDigit
for(int i=0;i<x.length;++i) {
x[i] = Math.round(complexArr[i].re * d) / d ;
}
}else {
for(int i=0;i<x.length;++i) {
x[i] = complexArr[i].re;
}
}
return x;
}
}2. fourier/Complex.java
package fourier;
public class Complex {
//I'd like to access data directly not using method.
public double re = 0;
public double im = 0;
public Complex(double re, double im) {
this.re = re;
this.im = im;
}
// return "2+3i" style string
public String toString() {
return toString("i");
}
// toString("j") --> "2+3j" style
public String toString(String im_ch) {
String s = "";
if(this.re==0 && this.im==0) {
s = "0";
}else if(this.re == 0) {
s = this.im + im_ch;
}else if(this.im == 0) {
s = "" + this.re;
}else if(this.im > 0) {
s = this.re + "+" + this.im + im_ch;
}else {
s = "" + this.re + this.im + im_ch;
}
return s;
}
}3. fourer/CMath.java
package fourier;
public class CMath {
public static Complex add(Complex z1, Complex z2) {
return new Complex(z1.re + z2.re, z1.im + z2.im);
}
public static Complex subtract(Complex z1, Complex z2) {
return new Complex(z1.re - z2.re, z1.im - z2.im);
}
public static Complex multiply(Complex z1, Complex z2) {
return new Complex(z1.re * z2.re - z1.im * z2.im, z1.re * z2.im + z1.im * z2.re);
}
public static Complex divideR(Complex z, double r) {
return new Complex(z.re / r, z.im / r);
}
public static double magnitude(Complex z) {
return Math.sqrt(z.re * z.re + z.im * z.im);
}
}4. test/Test_FFT.java
package test;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.util.Vector;
import fourier.*;
public class Test_FFT {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
test_simple_fft();
test_not_power_of_2();
test_measure_time();
test_use_file();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 1. test for simple a few data
private static void test_simple_fft() throws Exception{
double[] x = {0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1}; //input
Complex[] X; //result value after FFT calculation
System.out.println("** test_simple_fft **");
//1. calculate FFT for a few data. (count = 8)
X = FFT.fft(x);
for(int i=0;i<X.length;++i) System.out.print(X[i].toString()+", ");
System.out.println("");
//2. obtain FFT value with rounded format. and use "j" for imaginary character
X = FFT.fft(x,2); //rounded num_digit is 2
for(int i=0;i<X.length;++i) System.out.print(X[i].toString("j")+", ");
System.out.println("");
}
// 2. in case of 2^n count of data
private static void test_not_power_of_2() throws Exception{
double[] x = {0,0,0,0,1,1};; //input size is 6 that is not 2^n count
Complex[] X; //result value after FFT calculation
System.out.println("\n** test_not_power_of_2 (auto zero padding) **");
//1. in case of the input data size is not 2^n count.
// --> automatically fill zero and make input size 2^n count
X = FFT.fft(x,3);
for(int i=0;i<X.length;++i) System.out.print(X[i].toString()+", ");
System.out.println("");
}
// 3. measure execution time to 32k, 64k size data
private static void test_measure_time() throws Exception{
long beforeT, diffT;
int N = 0;
System.out.println("\n** test_measure_time **");
//1) 32kB data
N = (int)Math.pow(2, 15);
double[] data32 = new double[N];
for(int i=0;i<N;++i) data32[i] = Math.cos(2*Math.PI*0.004*i);
beforeT = System.currentTimeMillis();
Complex[] result32 = FFT.fft(data32);
diffT = System.currentTimeMillis() - beforeT;
System.out.println("Execution Time(32kB): " + diffT + "ms");
for(int i=0;i<4;++i) System.out.println("["+i+"]"+result32[i].toString()+", ");
System.out.println("......");
for(int i=N-4;i<N;++i) System.out.println("["+i+"]"+result32[i].toString()+", ");
System.out.println("");
//2) 64kB data
N = (int)Math.pow(2, 16);
double[] data64 = new double[N];
for(int i=0;i<N;++i) data64[i] = Math.cos(2*Math.PI*0.004*i);
beforeT = System.currentTimeMillis();
Complex[] result64 = FFT.fft(data64);
diffT = System.currentTimeMillis() - beforeT;
System.out.println("Execution Time(64kB): " + diffT + "ms");
for(int i=0;i<4;++i) System.out.println("["+i+"]"+result64[i].toString()+", ");
System.out.println("......");
for(int i=N-4;i<N;++i) System.out.println("["+i+"]"+result64[i].toString()+", ");
}
private static void test_use_file() throws Exception {
System.out.println("\n** test_use_file **");
//1) read file
Vector<String> v = new Vector<String>();
File f = new File("./data/input.txt");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f));
String line="";
while((line=br.readLine()) != null) {
line = line.trim();
if(line.length()!=0) v.add(line);
}
br.close();
//2) parse string to double
double[] x = new double[v.size()];
for(int i=0;i<x.length;++i) x[i] = Double.parseDouble(v.get(i));
//3) do fft
long beforeT = 0, diffT=0;
beforeT = System.currentTimeMillis();
Complex[] X = FFT.fft(x);
diffT = System.currentTimeMillis() - beforeT;
System.out.println("fft calculation time: "+diffT+"ms");
//4. save Y to the file
f = new File("./data/outptu_fft.txt");
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(f));
if(f.isFile() && f.canWrite()) {
for(int i=0;i<X.length;++i) {
bw.write(X[i].toString());
bw.newLine();
}
}
System.out.println("fft result is written to the file");
bw.close();
}
}5. data/input.txt
input.txt
0.20MB
The project files for Eclipse with including whole source code. (used Eclipse version is 2021-09)
FFT.zip
0.27MB
- The End -
| 이전글: 07-6. Java로 FFT 알고리즘 충실히 구현하기 |
| 다음글t: 07-7. C로 짠 FFT Code |
반응형
'푸리에 변환, 신호 > 푸리에 변환의 모든 것' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [07-7 Code]FFT source code for C (0) | 2022.08.07 |
|---|---|
| 07-7. C로 짠 FFT Code (1) | 2022.08.07 |
| 07-6. Java로 FFT 알고리즘 충실히 구현하기 (0) | 2022.08.05 |
| [07-5 Code] Fastest FFT code for Java (0) | 2022.08.05 |
| 07-5. 가장 빠른 Java용 FFT 구현해보기 (2) | 2022.08.05 |